Biography
- Fangyu Liu received the B.S. degree in software engineering from the University of South China, Hengyang, China, in 2020, and the M.S. degree in computer application technology from Shanghai University, Shanghai, China, in 2023. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree in computer application technology at the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China. His current research interests include biomedical signal processing, sensor information fusion, wearable health-monitoring devices, medical image analysis, and machine learning.
Research Interests
- Biomedical Signal Processing
- Sensor Information Fusion
- Wearable Health-monitoring Devices
- Medical Image Analysis
- Machine Learning
Education
- 2023.09 - Present: Ph.D., Computer Application Technology, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 2020.09 - 2023.06: M.S., Computer Application Technology, School of Computer Engineering and Science, Shanghai University (Recommended Exam-exempted Post-graduate)
- 2016.09 - 2020.06: B.S., Software Engineering, School of Computer / School of Software, University of South China (Outstanding Engineer Education and Training Program)
Working Experience
- 2023.09.19 - 2024.05.07:A student co-trained by BGI-shenzhen
- 2019.11.15 - 2020.02.15:Intern at Nuclear Industry Engineering Research and Design Co., LTD
Projects
-
Topic: Research on wearable intelligent sensing and computing methods for individualized sports health [Link]
Source: Shenzhen International Cooperation Project
Date: 2023 - 2025
Duty: Student participation
-
Topic: Tensor-based multimodal data fusion with causal reasoning and interpretable aid diagnosis for Alzheimer's disease [Link]
Source: Key Program for International Science and Technology Cooperation Projects of China
Date: 2024 - Present
Duty: Student participation
Recent Publications [All]
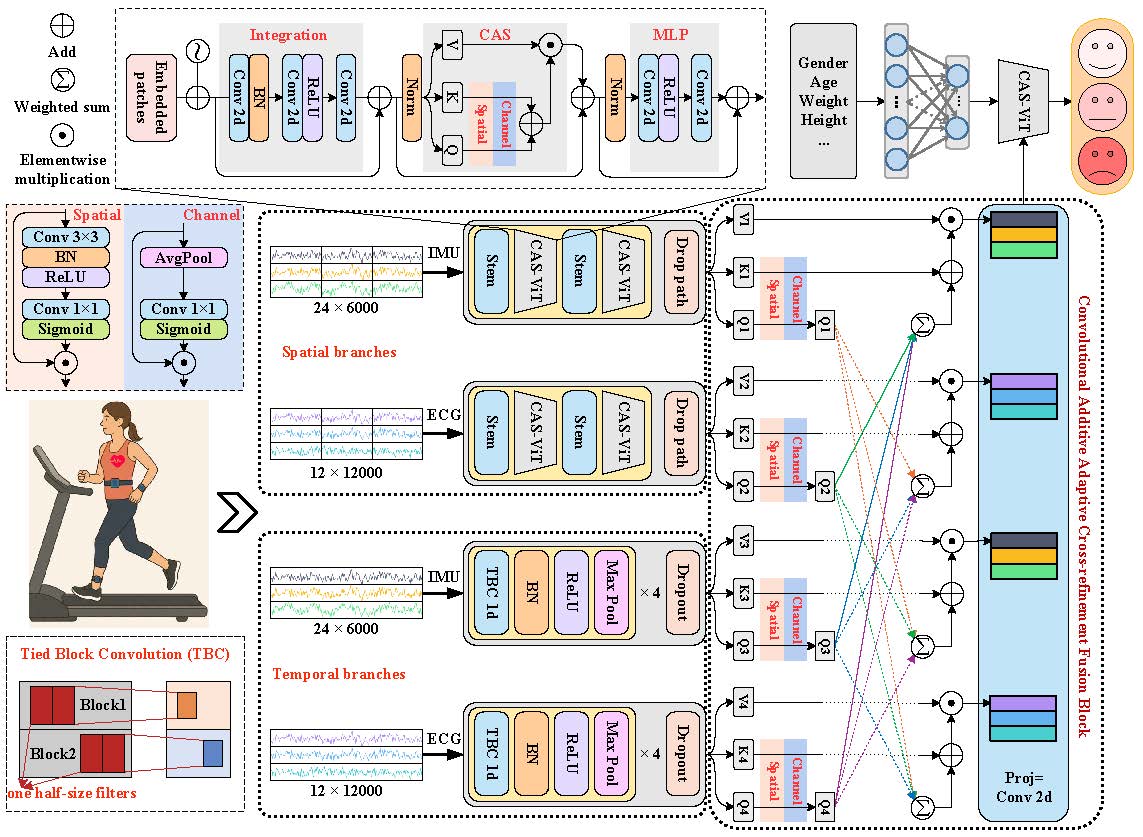
Accurate objective physical fatigue (OPF) assessment is essential for industrial safety, athletic optimization, and health management. While wearable multisource fusion methods are emerging for OPF monitoring, they face three key challenges: inadequate spatial modeling, inefficient multimodal fusion, and limited long-range dependency capture. To address these limitations, we propose DBMNet - a dual-branch multimodal network for fatigue level classification that separately extracts temporal dynamics and spatial patterns from raw 12-lead ECG and multi-site IMU signals. Our novel Convolutional Additive Adaptive Cross-refinement Fusion (CAACF) module enables adaptive and interpretable fusion of heterogeneous modalities. Using synchronized ECG-IMU data from 65 subjects during graded treadmill exercise with coarse and fine-grained fatigue annotations, experiments show DBMNet achieves up to 7% accuracy improvement over state-of-the-art methods across multiple metrics. The lightweight architecture ensures deployability on mobile and wearable devices, providing an effective framework for real-time fatigue monitoring using multi-source physiological signals.
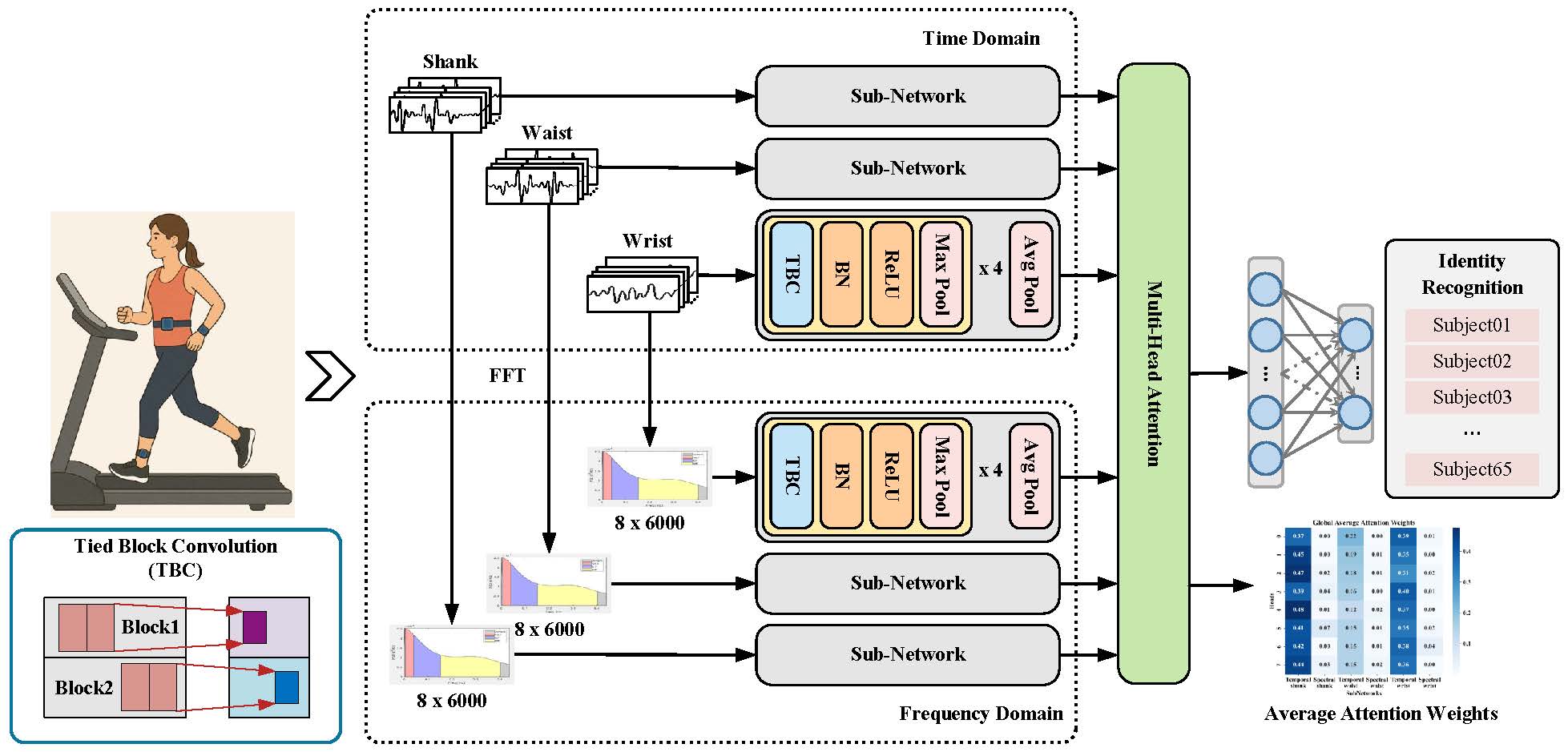
IMU-based gait biometrics have gained attention for unobtrusive identity recognition, yet the actual contributions of different sensor positions and signal modalities remain unclear. This study presents a comprehensive quantitative analysis of IMU placements (shank, waist, wrist) and feature domains (time and frequency) for identity recognition. Using an attention-gated fusion network to adaptively weight signal branches, experiments reveal the shank IMU dominates recognition accuracy while waist and wrist sensors provide auxiliary information. Time-domain features contribute most to classification performance, with frequency-domain features offering complementary robustness. These findings provide crucial guidance for sensor and feature selection in designing efficient wearable identity recognition systems.
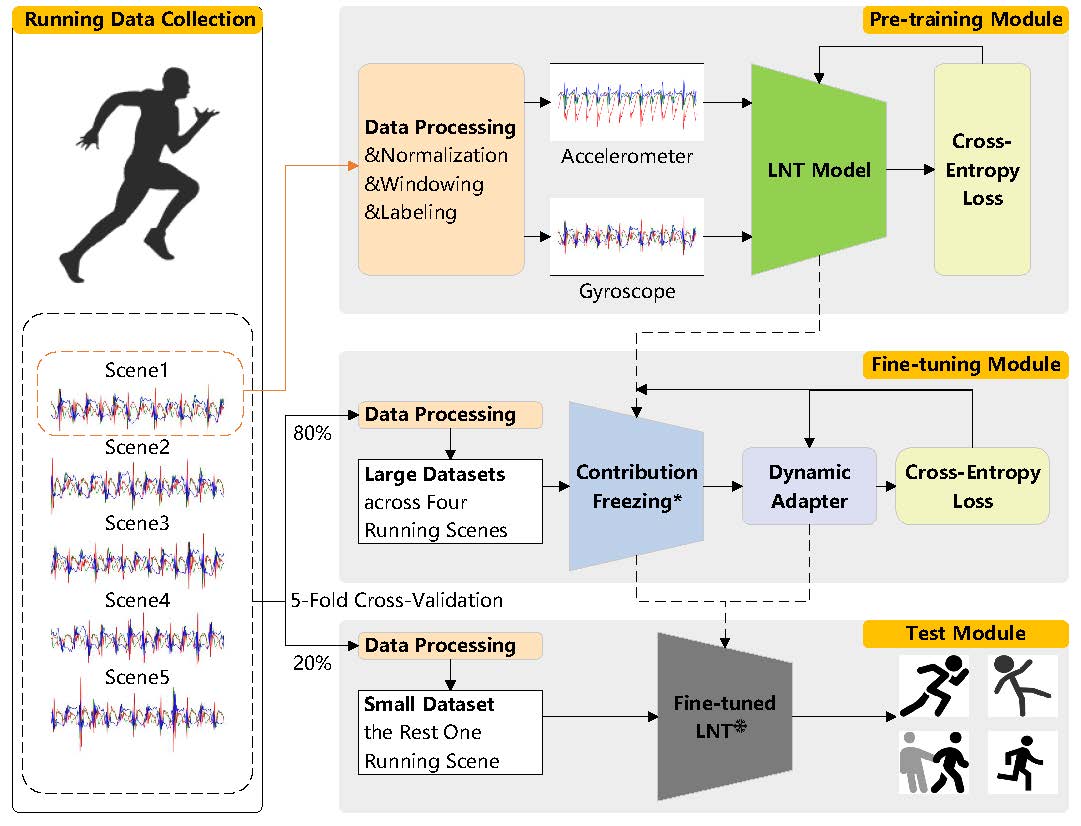
This paper proposes a Cross-Scenario Transfer Learning (CSTL) framework to address the poor adaptability and high complexity of deep learning-based abnormal running posture detection using wearable inertial sensors. The framework includes: (1) A LightNorm Transformer (LNT) model pre-trained on single-scenario data for initial feature extraction; (2) A fine-tuning stage with contribution-guided freezing and dynamic adapters to transfer the model to five running scenarios, evaluated via leave-one-out cross-validation. Results show that CSTL achieves 87.01% accuracy with only 10 fine-tuning epochs, outperforming non-transfer methods and optimizing the accuracy-efficiency trade-off. The solution enhances robustness for real-world applications.
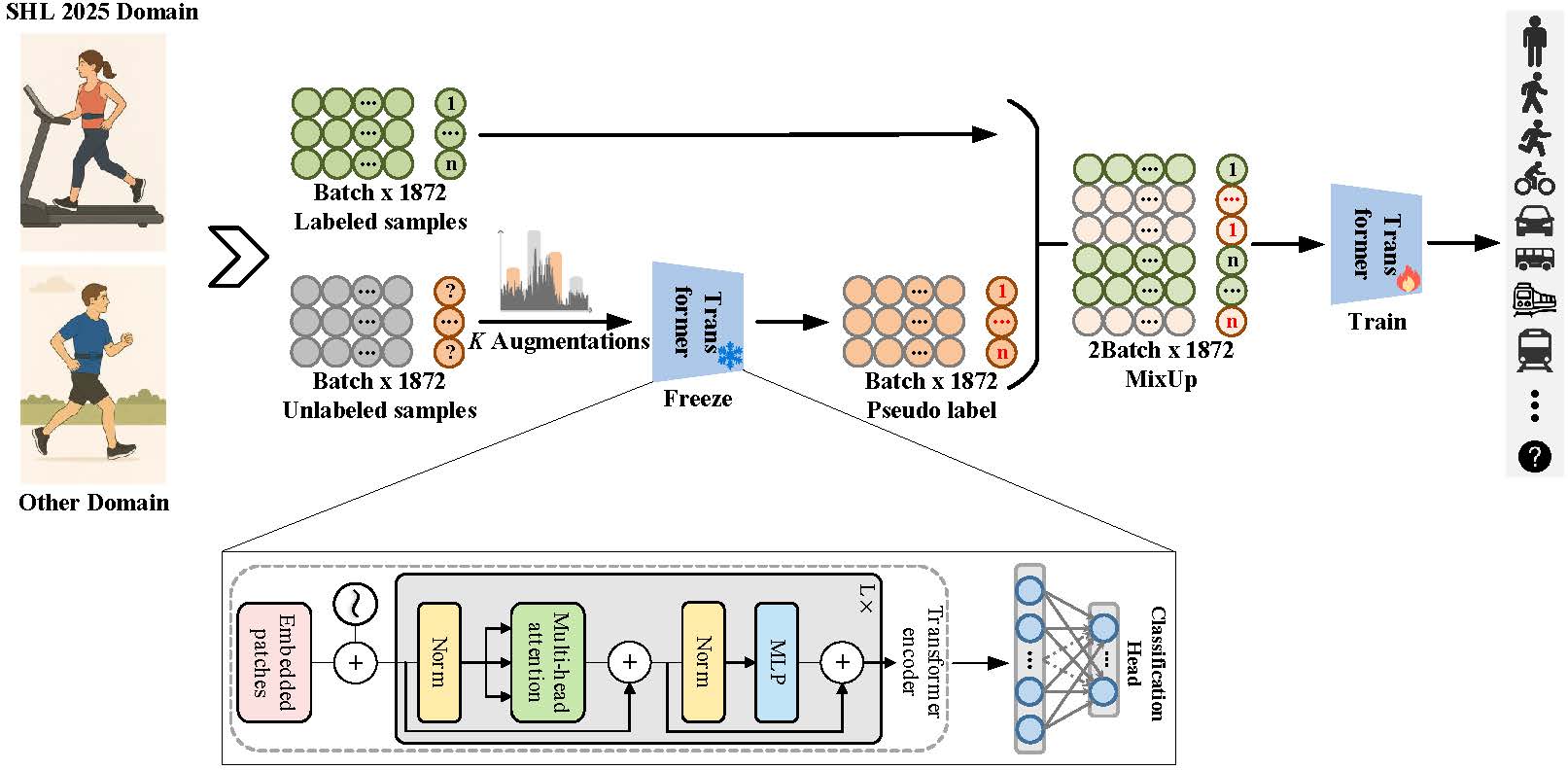
Cross-domain human activity recognition using wearable inertial sensors remains a challenging task, especially in scenarios where no labeled data is available in the target domain. To address this, our team (SIAT-BIT) propose a semi-supervised learning framework based on MixMatch for locomotion and transportation mode recognition. Our approach leverages labeled data from multiple public HAR datasets and unlabeled data from the Sussex-Huawei Locomotion-Transportation Recognition Challenge Task 2 (Kyutech IMU) dataset. The framework integrates pseudo-label generation, data augmentation, soft label sharpening, and cross-sample mixing to mitigate domain shift and label scarcity. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves competitive performance in Task 2 with an accuracy of 76.8% and F1 score of 76.5%, confirming its effectiveness in modeling real-world cross-domain activity scenarios without relying on target domain labels.
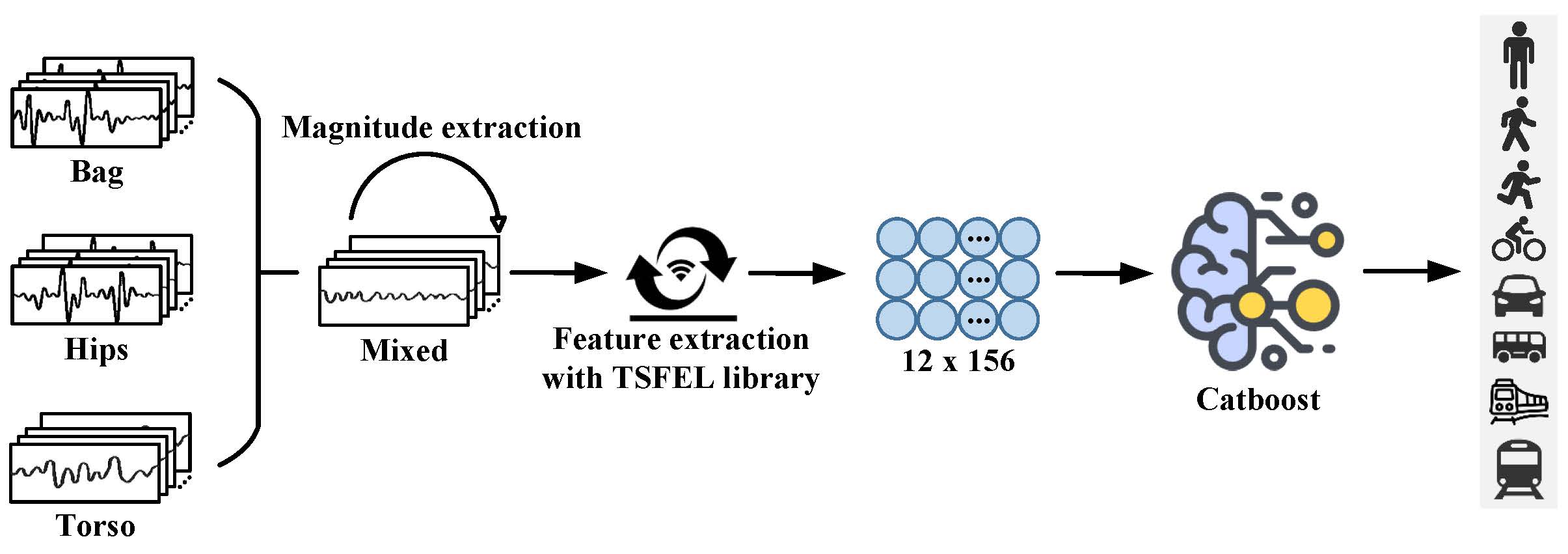
Human Activity Recognition has been widely applied in mobile analysis, mobile health, and intelligent sensing. However, the existing HAR algorithms still face challenges in sensor modality dropout, varying device placement, and limited model generalization. To address these issues, the Sussex-Huawei Locomotion (SHL) recognition challenge provides a complex real-world dataset for algorithm development. In this study, our team (SIAT-BIT) proposes a classification framework based on handcrafted features, extracting 156 statistical, time-domain, and frequency-domain features from a total of 12 channels, including the tri-axial signals and their amplitudes of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers. The experimental results show that our approach achieves strong recognition performance across multiple device placements, achieving an accuracy rate of 71.4% and an F1 score of 71.8% on the verification dataset which confirms the effectiveness and efficiency of our method.
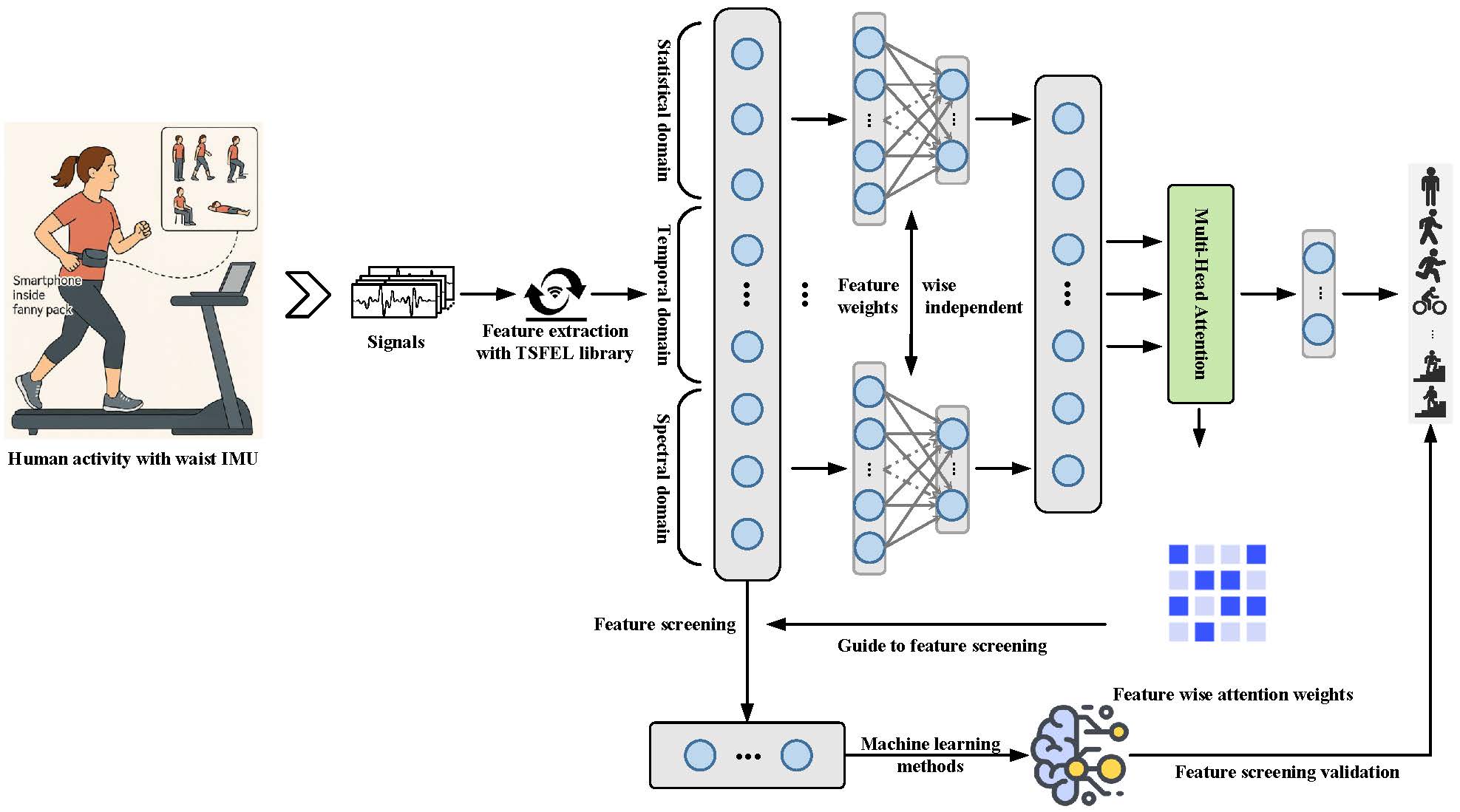
Human activity recognition (HAR) using wearable sensors is crucial for ubiquitous computing applications in healthcare, fitness monitoring, and smart environments. Sensor-based HAR faces challenges from high-dimensional, multi-channel time series data containing redundant or irrelevant features that degrade performance and interpretability. We propose a lightweight feature screening framework guided by multi-head attention to address this. The model employs channel-wise linear transformations to extract localized representations from each sensor axis, then uses a multi-head attention module to dynamically assess feature importance across channels. This approach emphasizes informative components while suppressing noise and redundancy. On the KU-HAR dataset, our method achieves 96.0% accuracy using only 60 selected features. The selected features also provide valuable references for future research in feature selection, model simplification and multimodal sensor fusion.
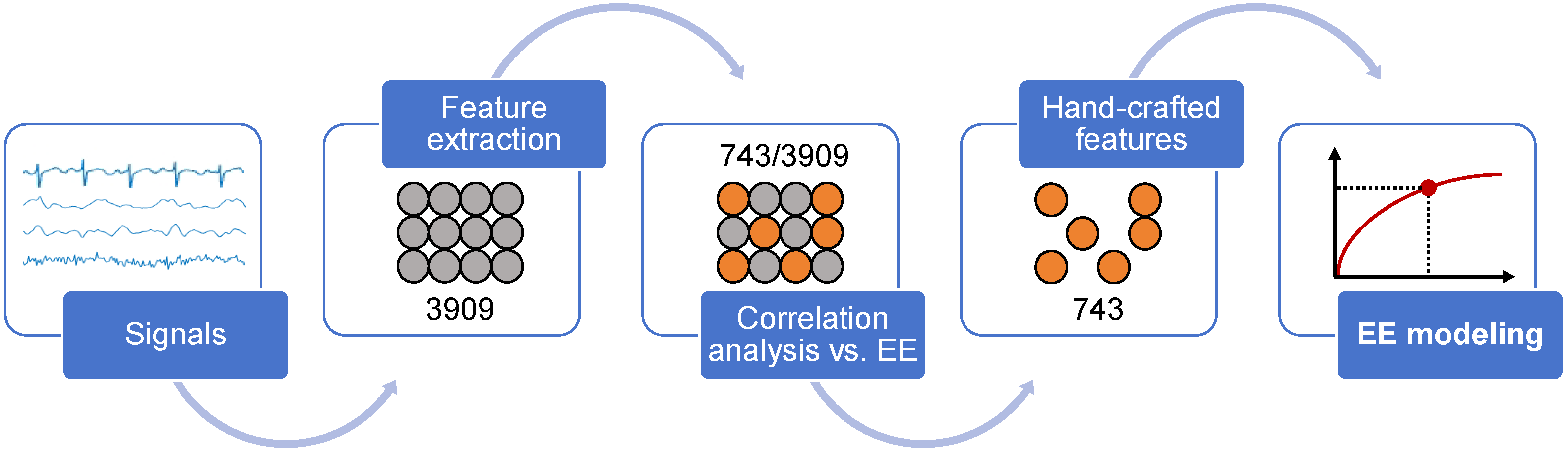
This study addresses the interpretability limitations of deep learning-based wearable energy expenditure monitoring by developing an explainable regression model for real-time running energy prediction. Through systematic analysis of demographic, physical activity and physiological features, the research proposes a novel hand-crafted feature selection method identifying 743 key features. Among various machine learning algorithms tested, Gradient Boosted Regression (GBR) achieved optimal performance (CC=0.970, RMSE=1.004, MAE=0.729) in five-fold cross-validation with 34 volunteers. The study not only accomplishes accurate real-time energy expenditure prediction but also provides a new technical approach combining manual feature engineering with interpretable algorithms for sports monitoring applications.
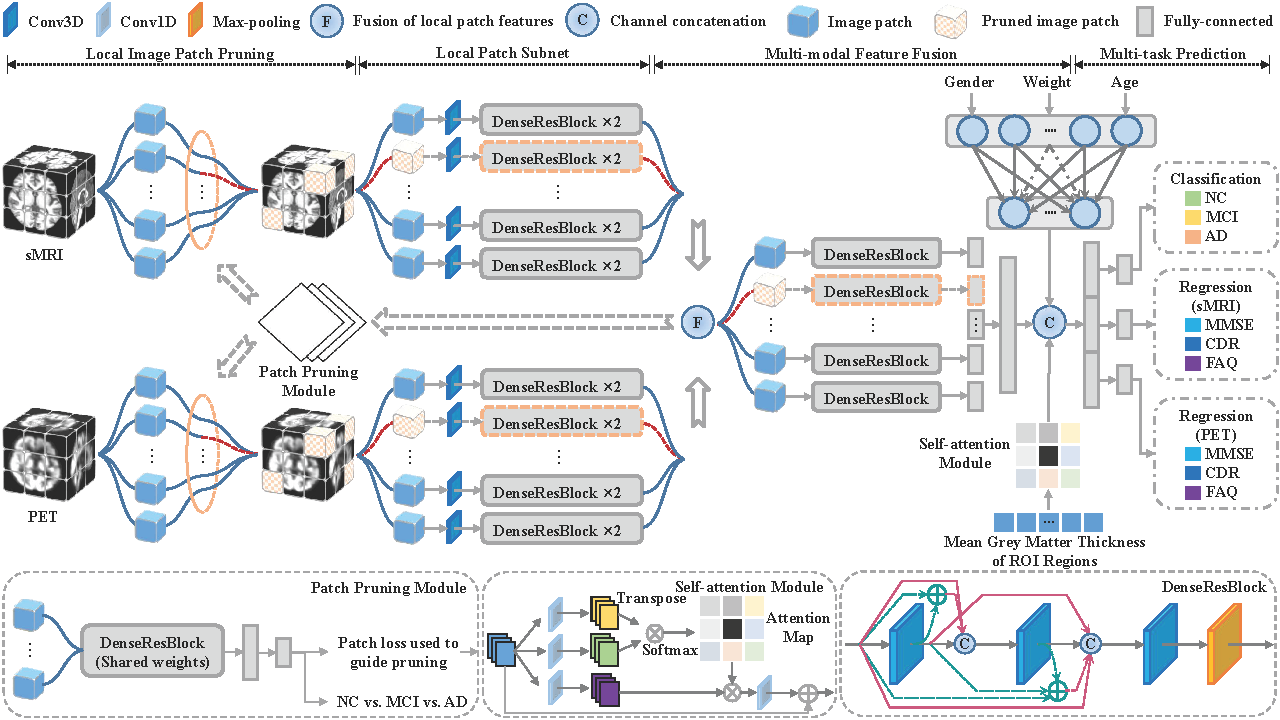
This study proposes an innovative Multi-Task Joint Learning Network (MTJLN) to address key challenges in brain disease diagnosis and clinical score prediction. The method divides brain images into 216 local patches covering all potential lesion areas and employs a patch pruning algorithm to automatically select informative regions, overcoming the limitations of pre-determining discriminative locations. The novel framework integrates fine-grained patch-based multimodal features with coarse-grained non-image features at intermediate layers, effectively utilizing intrinsic correlations between multimodal data and multitask variables. A specially designed weighted loss function enables the inclusion of subjects with incomplete clinical scores, significantly improving data utilization. Experiments on 842 ADNI subjects demonstrate the method's effectiveness in predicting pathological stages and clinical scores, providing a new solution for precise brain disease diagnosis and progression assessment.
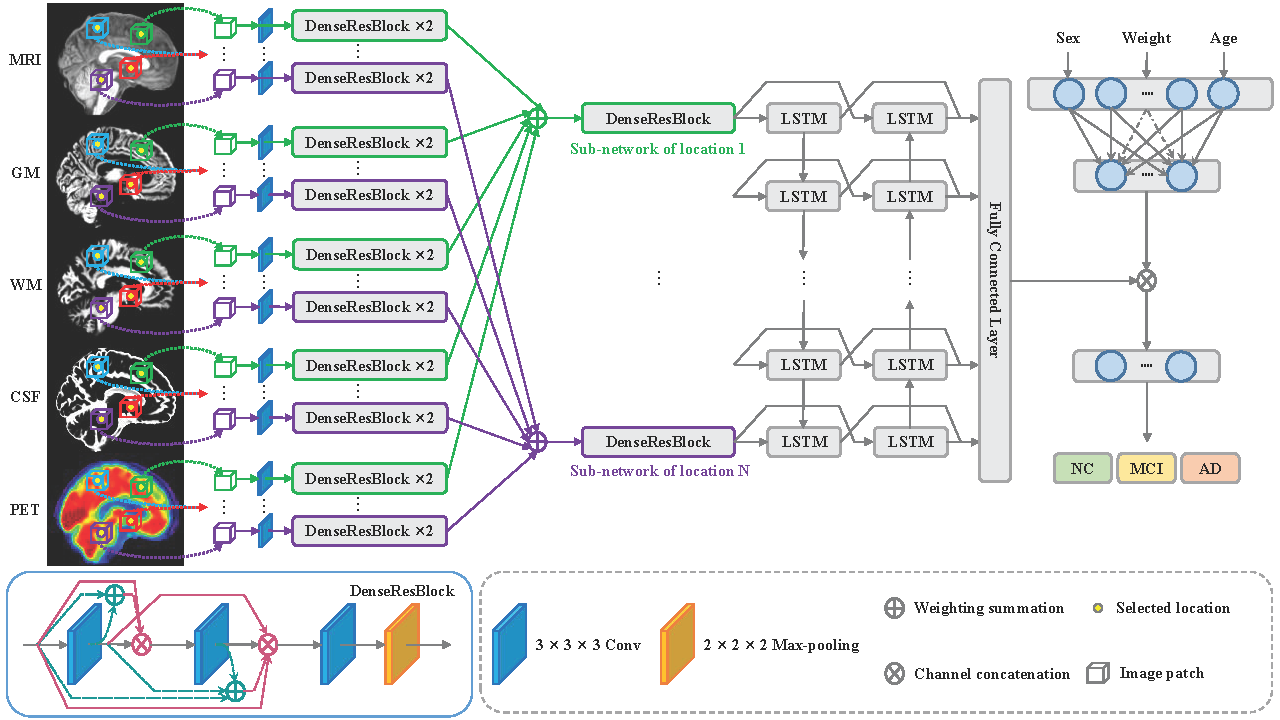
This study addresses the limitations of single-modality methods and spatial information loss in patch-based approaches for Alzheimer's disease (AD) diagnosis by proposing a Patch-based Deep Multi-Modal Learning (PDMML) framework. The framework features a prior-free discriminative location discovery strategy to automatically identify potential lesion areas, eliminating reliance on anatomical landmarks and expert experience. It innovatively integrates multimodal features at the patch level to capture comprehensive disease representations while preserving spatial information through joint patch learning, overcoming the flattening-induced information loss. Evaluated on 842 ADNI subjects, PDMML demonstrates superior performance in both discriminative region localization and brain disease diagnosis, offering a robust computer-aided solution for early mild cognitive impairment (MCI) detection.
Academic Service
Reviewer
- Reviewer for the journal "IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics"
- Reviewer for the journal "Knowledge-Based Systems"
- Reviewer for the journal "Scientific Reports"
- Reviewer for the journal "The Journal of Supercomputing"
- Reviewer for the 21st IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing (UIC 2024)
Volunteer
- Volunteer for the 15th ACM Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology, and Health Informatics (ACM BCB 2024)
- Volunteer for the national science-popularizing public activity--"the 20th Public Science Day held by the Chinese Academy of Sciences"
Honors and Awards
- 2024-2025, Merit Student of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 2020, Outstanding Graduates of Hunan Province, China
- 2020, Outstanding Graduates of the University of South China
- 2017-2018, National Encouragement Scholarship
- 2017-2018, Merit Student of the University of South China
- 2016-2017, Merit Student of the University of South China
- 2015, Merit Student in high school
